What is the formula for photosynthesis
What is photosynthesis
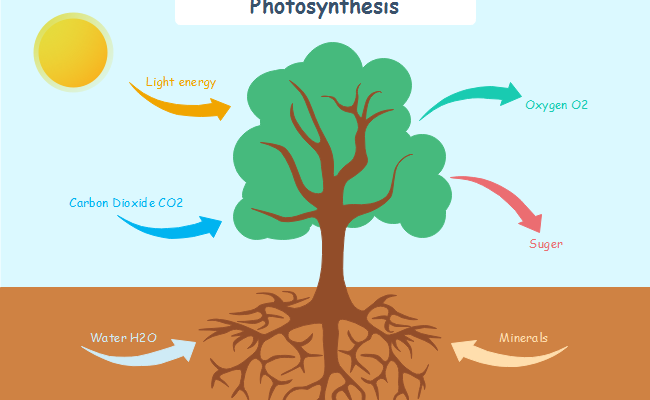
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process that occurs in the cells of plants, algae, and some bacteria. It is the process by which these organisms convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose or other carbohydrates. Photosynthesis takes place in specialized cellular organelles called chloroplasts.
Key stages of photosynthesis include:
- Light Absorption:
- Chlorophyll pigments in chloroplasts absorb light energy from the sun.
- Water Splitting (Photolysis):
- Water molecules are split into oxygen, protons (H⁺), and electrons during the light-dependent reactions. Oxygen is released as a byproduct.
- ATP and NADPH Production:
- The energy from the absorbed light is used to generate ATP and NADPH, which are energy carriers.
- Carbon Fixation (Calvin Cycle):
- In the light-independent reactions, carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules through a series of enzyme-mediated reactions.
- Glucose Production:
- The fixed carbon dioxide is ultimately used to synthesize glucose and other carbohydrates.
- Oxygen Release:
- Oxygen produced during the water-splitting stage is released into the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis is essential for the survival of plants and the ecosystems that depend on them. It not only provides plants with the energy needed for growth and maintenance but also contributes to the oxygen levels in the Earth’s atmosphere. Additionally, photosynthesis forms the basis of the food chain, as plants are the primary producers that support various organisms in the ecosystem.
What is the formula for photosynthesis
The overall chemical equation for photosynthesis is represented as follows:
6CO2+6H2O+Light Energy→C6H12O6+6O2
In words, this equation indicates that carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), in the presence of light energy, undergo a series of complex biochemical reactions within chloroplasts to produce glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and oxygen (O₂).
Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages: the light-dependent reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membranes, and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle), which occur in the stroma of chloroplasts. The overall process is essential for the conversion of light energy into chemical energy that sustains the life of plants and many other organisms on Earth.